FDIC Reports Large Gains for Financial Institutions in Third Quarter


The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) announced banks and other financial institutions posted their highest profits in Q3 in six years. The improvement marks a 6.6 percent increase in aggregate net income from the same time last year, with an average return on assets at 1.06 percent. The institutions pulled a total profit of $37.6 billion dollars.
The FDIC’s Quarterly Banking Profile also reported that bank failures had fallen to a four-year low – 12 institutions failed while 49 were merged or absorbed by other entities. Of the FDIC’s 7,181 insured institutions, fewer than 700 are described as “problem” institutions, its lowest number in three years. Problem institutions are defined as having managerial, financial, or operational weaknesses and are characterized by having a high potential for failure or requiring acquisition.
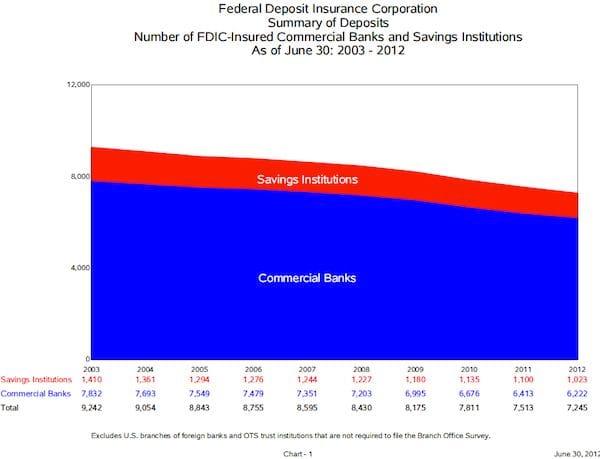
Most importantly, deposits in the third quarter totaled $10 trillion, a growth of 1.8 percent from last quarter. Deposits are an important economic marker, as they essentially determine whether or not banks can lend more money and, thus, continue to push money through the market. Increased velocity of money tends to stimulate economic growth. According to the FDIC profile, deposits funded 73.9 percent of the banking industry’s assets. This is the highest proportion of deposits to assets since the fourth quarter of 1993.
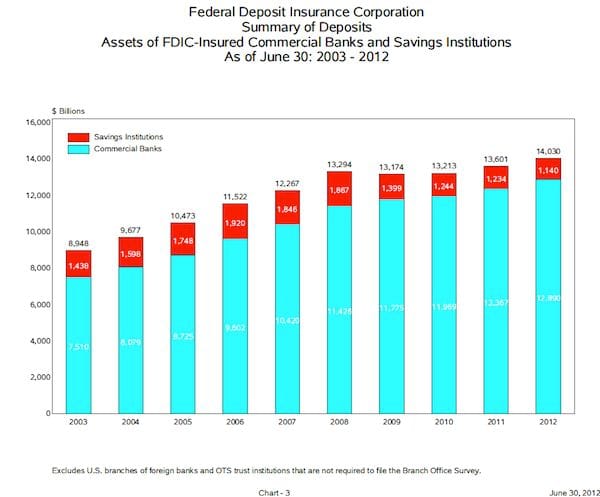
While these numbers seem promising, the market is still exercising caution. FDIC Chairman Martin Gruenberg noted that the gains were merely modest, particularly as reserves have actually decreased since 2011. "This was another quarter of gradual but steady recovery for FDIC-insured institutions," said Gruenberg, "Signs of further progress were evident in a number of indicators, such as loan growth, asset quality and profitability." Banks are generating most of their revenue from loan sales, which could be a sign of an improvement, but economists remain unsettled by the wide ranging discrepancy amongst institutions in growth and loss.