Rand Paul Tops GOP Field in Republican Liberty Caucus Straw Poll
The Center for Election Science (CES) recently handled the Republican Liberty Caucus straw poll, where Rand Paul topped Ted Cruz for first. And once again, approval voting demonstrated its superiority over the ubiquitous choose-one plurality voting.
Approval voting lets voters choose as many candidates as they like, avoiding the typical pitfalls of our choose-one plurality voting. The fact that the Republican Liberty Caucus chose to release the approval voting results as the main poll results is telling.
Here’s a look at what voters had in front of them for the poll:
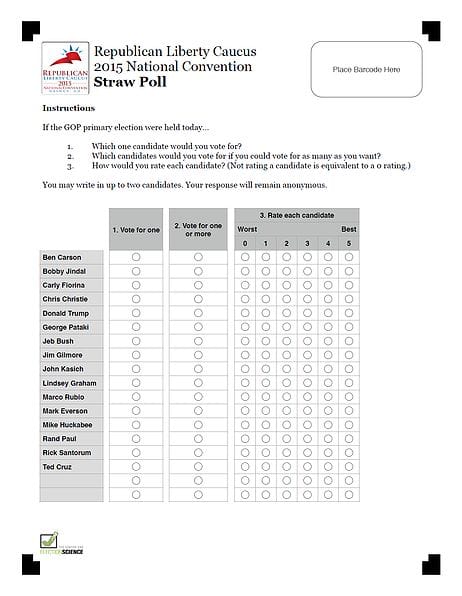
All 779 voters were asked to vote three different ways: (1) The standard choose-one plurality method, which causes vote splitting; (2) approval voting, which lets voters pick as many candidates as they want; and (3) score voting, which lets voters score candidates on a scale.
Which method voters used made a big difference. Just have a look (score voting is shown here as a percentage of maximum score for comparison purposes; “W” indicates a write-in):
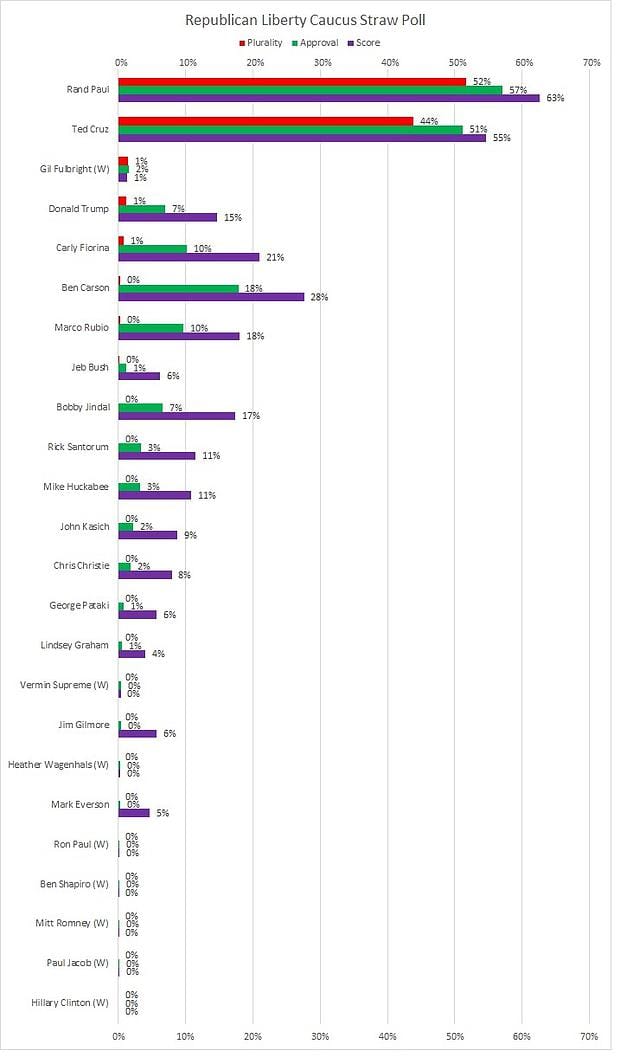
Paul and Cruz happened to get proportionately similar results in both plurality and approval voting, though that’s not always the case. What’s striking, however, is the difference among the other candidates. Without approval or score voting, the remaining candidates would be indistinguishable. With these better voting methods, however, you see multiple candidates stand out.Carson, Fiorina, and Rubio, all get roughly 10% approval or above while Jindal and Trump begin to show their existence with the more nuanced score voting. Under choose-one plurality, however, they’re indistinguishable from the rest of the pack at 1% or less.
So why does traditional choose-one plurality give artificially low results while approval voting gives a clearer picture? CES chair Dr. Andrew Jennings summarized the answer to the Washington Examiner: “[Approval voting] prevents spoilers and lets all candidates see their true level of support by preventing the vote from being split in a crowded Republican field.”
Many candidates otherwise get artificially low support because our choose-one plurality ballot doesn’t let voters provide any information. It’s not until we remove the choose-one restriction that they’re actually able to have a say about the other candidates.
Now here’s the obvious question. If using approval voting fixes straw polls, then why do parties continue using a choose-one plurality method for their primaries?
[Link to ballot data] [Video for checking ballot data] [Check your 3-digit ballot]
Ballots choosing a candidate under plurality were also given approval for that candidate for internal consistency.
Editor's note: This article originally published on The Center for Election Science's blog on October 15, 2015, and has been modified slightly for publication on IVN.
Photo Credit: Christopher Halloran / Shutterstock.com