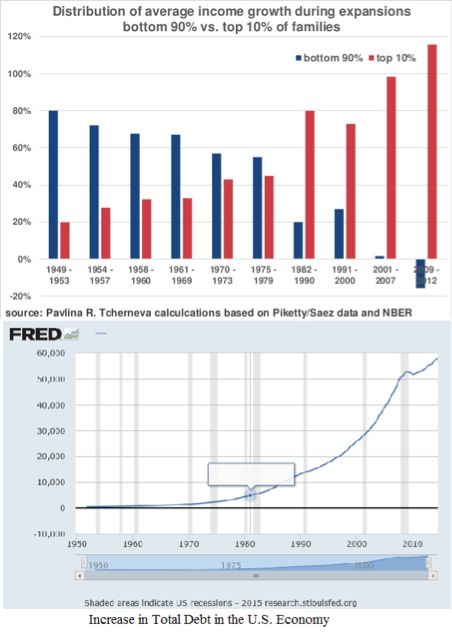
Growth in Income Inequality vs. Growth in Total Debt

A recent study on the growth of wealth inequality instantly drew the usual finger pointing and denials between hardcore political opponents even though the chart clearly shows a steady trend across all administrations of either party.
As a result, the usual arguments about the failure of trickle-down economics and the failure of tax and spend policies fall short. But the bickering continues.
There is one comparison that shows a correlation stronger than smoking and lung cancer between one negative economic trend and the inequality trend; namely, the growth of total debt in the economy as presented by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
As more people and companies and governments borrow more money to buy goods and services, they have less actual cash available to spend. Eventually, the economy slips into a recession and the government’s response over the last 50 years has been to print money and encourage more borrowing to get the economy going again.
But as the debt accumulates, the return on increasing the debt is reduced.
So how do the wealthy actually benefit from this? The very low interest rates being used by the government to encourage more lending and the money being printed to buy debt from the banks all works to put more cash in the hands of the big investors who put it into assets such as stocks and real estate. This drives the prices up, which makes them wealthier.
But it does nothing to increase demand for goods and services, resulting in limited job growth and stagnant wages. The thing is, all that wealth increase for the top one percent is on paper, or in data bits in virtual space. When the borrowing stops, which it eventually must, the asset prices collapse and the paper wealth disappears as fast as it was created.
The key event that pushed our economic future past the point of no return occurred in 1971 when the United States left the Bretton Woods agreement, removing the link between the U.S. dollar and the world gold standard. This freed the U.S. to print and borrow as much as it wanted to as long as the rest of the world maintained “full faith and credit” in the U.S. economy. The result -- as seen in the above charts -- is obvious and dramatic. It is not a partisan problem and there is no partisan fix, which is probably why neither side talks about it much.
Photo Credit: Ai825 / shutterstock.com